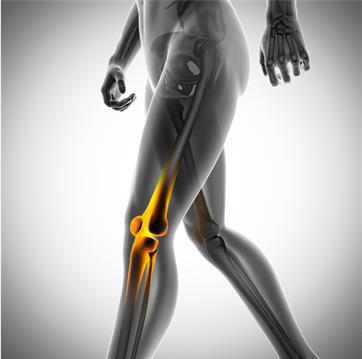
 Rheumatoid arthritis, also known as RA, is an autoimmune disease. Normally your body’s immune system makes antibodies which attack bacteria and viruses to help fight infection. In the case of rheumatoid arthritis, these antibodies are sent to the lining of the joints where they mistakenly attack the surrounding tissue and the joint [1].
Rheumatoid arthritis, also known as RA, is an autoimmune disease. Normally your body’s immune system makes antibodies which attack bacteria and viruses to help fight infection. In the case of rheumatoid arthritis, these antibodies are sent to the lining of the joints where they mistakenly attack the surrounding tissue and the joint [1].
The main symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis are:
Joint pain – usually first thing in the morning or after a period of inactivity
Stiffness – joints may feel stiff first thing in the morning or after a period of inactivity
Swelling, warmth and redness – the lining of affected joints may become inflamed, causing swelling and making them hot and tender to touch [2].
These symptoms may be accompanied by more generic symptoms:
Tiredness and a lack of energy
High temperature (fever)
Sweating
Poor appetite
Weight loss [2]
There is currently no cure for rheumatoid arthritis and current treatments are symptomatic. Current treatments can help prevent and slow joint damage and reduce inflammation and relieve pain giving sufferers a more active life [3].
While there is no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, scientists are currently conducting 26 clinical trials which are investigating the application of stem cells in RA [4], giving sufferers hope of a more effective therapy being found in the future.
If you think you or someone you know may be suffering with RA please visit your GP or medical practitioner for further advice.
[1] http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Rheumatoid-arthritis/Pages/Causes.aspx
[2] http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Rheumatoid-arthritis/Pages/Symptoms.aspx
[3] http://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Rheumatoid-arthritis/Pages/Treatment.aspx
[4] https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=stem+cells+rheumatoid+arthritis&Search=Search